Think back to your school science lessons. Remember those litmus papers that turned red or blue based on whether something was acidic or basic? That was your first introduction to the pH scale. But what exactly is it, you ask?
Well, in simple terms, the pH scale is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
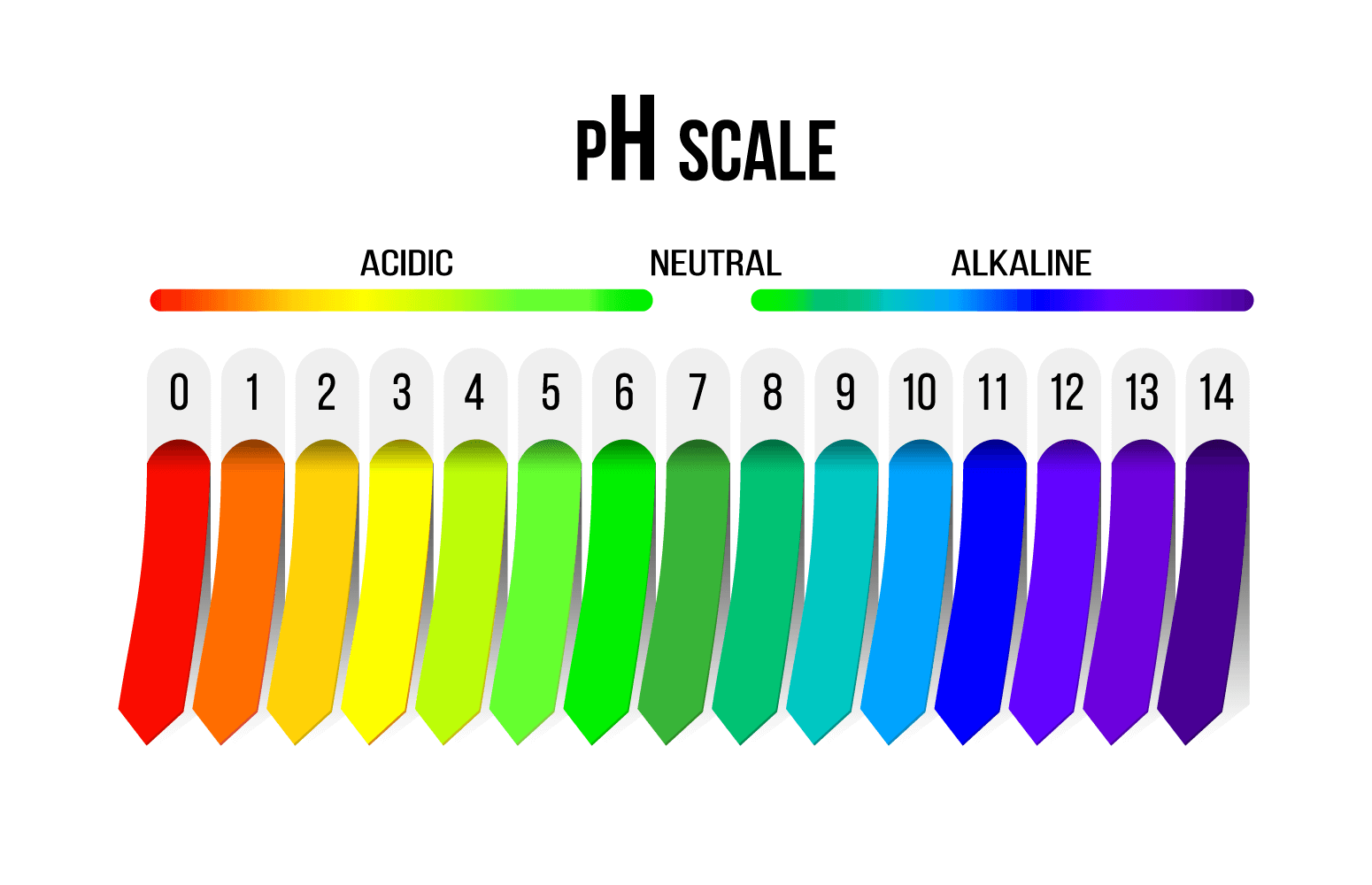
The term pH stands for ‘potential of hydrogen’. It measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. The scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Anything below 7 is considered acidic, while anything above 7 is considered basic or alkaline.
Don’t worry, we’re not about to launch into a chemistry lecture – this is more like a friendly chat about the pH scale, with a bit of humor and science thrown in for good measure.
So, strap on your science goggles, grab your lab coat, and get ready to dive into the intriguing and (literally) colorful world of the pH scale.
pH Levels: What Makes a Substance Acidic or Basic?
To explain what makes a substance acidic or basic, let’s take the example of our morning cup of coffee (or tea for the non-coffee drinkers among us). Coffee is considered slightly acidic with a pH level below 7. But why is that?
Well, when coffee beans are roasted and brewed, they release hydrogen ions. The more hydrogen ions a solution has, the more acidic it is and the lower its pH level.
On the other hand, a substance like baking soda is considered basic because it has fewer hydrogen ions and a higher pH level.
But don’t worry, you don’t need to do a science experiment every time you make coffee. Instead, you can use a pH chart to determine the acidity or alkalinity of common substances.
How to Read and Understand a pH Chart
Reading a pH chart is like reading a map. The chart usually has colors and numbers that correspond to different pH levels. The colors range from red (acidic) to purple (basic), with green being neutral.
Imagine it like a rainbow, but instead of leading you to a pot of gold, it leads you to a better understanding of acidity and alkalinity.
If you were to place different substances on this chart, lemon juice would be somewhere around 2 (very acidic), while bleach would be around 13 (very basic). Water, being neutral, would be smack dab in the middle at 7.
On this scale, each number represents a tenfold difference in acidity or alkalinity.
For instance, a pH of 3 is ten times more acidic than a pH of 4, and a hundred times more acidic than a pH of 5. Cool, right?
Remember, lower numbers mean more acidic, and higher numbers mean more basic.
Understanding a pH chart can help you make informed decisions, whether you’re gardening, cooking, or taking care of your health.
How to Measure pH Levels
Measuring pH levels can be as simple as dipping a piece of litmus paper into a solution and checking the color change. Remember those red and blue strips from your science class? Those were litmus papers.
However, for more accurate results, you might want to use a pH meter. A pH meter is a device that measures the hydrogen ion concentration in solutions, thus determining their acidity or alkalinity. This handy tool is used in various industries, from food and beverage to healthcare.
But before we dive into the practical applications, let’s get a better understanding of the pH scale and balance.
The Science Behind pH Levels and pH Balance

The science behind pH levels and pH balance is all about hydrogen ions. Remember that the ‘H’ in pH stands for hydrogen. The more hydrogen ions a substance has, the more acidic it is. Conversely, the fewer hydrogen ions, the more basic or alkaline it is.
Maintaining the right pH balance is crucial in many areas. For instance, in your body, a slightly alkaline pH of 7.4 is ideal for your blood. If this balance is thrown off, it can lead to health problems. Similarly, different plants require different soil pH levels to grow properly. As the pH scale is logarithmic, even small changes in pH can make a big difference.
That’s why understanding and monitoring your environment’s or body’s pH levels can be so important. Knowing the right range for your specific needs can help you take preventive measures and avoid potential problems down the line.
Now, let’s look at how this knowledge is applied in various industries.
Practical Applications of pH Level Chart in Various Industries
The pH level chart isn’t just a pretty rainbow of colors. It has practical applications in various industries. Here are some key examples:
Food and Beverage Industry: The pH level chart is commonly used in the food and beverage industry to ensure product safety and quality. For example, the pH level of dairy products such as cottage cheese must be carefully monitored to prevent spoilage and growth of harmful bacteria. Similarly, in brewing and winemaking, maintaining the right pH level contributes significantly to the taste, aroma, and color of the final product.
Swimming Pool Maintenance: pH level plays a crucial role in swimming pool maintenance. A low pH indicates acidity which can corrode metal equipment, cause skin irritation and reduce the effectiveness of chlorine. A high pH, on the other hand, can cause scaling on the pool surface and cloudy water. Therefore, using a pH chart helps in maintaining the required pH levels, typically between 7.2 and 7.8.
Agriculture and Gardening: In agriculture and gardening, a pH level chart is useful in soil testing. The pH level of soil can affect nutrient availability and thus plant health. For instance, if the soil is too acidic or too basic, certain nutrients get locked up and are not as easily available to the plants.
Cosmetics Industry: In the cosmetics industry, the pH level of products like creams, lotions, and shampoos is checked to ensure skin compatibility. For instance, the pH of our skin is slightly acidic (5.5), so any product with a much higher or lower pH can disrupt the skin’s natural barrier and cause irritation.
Pharmaceutical Industry: The pharmaceutical industry often uses pH charts in the development and manufacturing of drugs. Certain drugs need a specific pH to be effective and stable. Also, during formulation and manufacturing, maintaining the correct pH is critical for product stability and shelf life.
Water Treatment: In water treatment plants, pH levels need to be monitored and adjusted to prevent pipe corrosion and to optimize disinfection. For example, drinking water should generally have a pH between 6.5 and 8.5 to be safe and palatable.
Textile Industry: The textile industry uses pH level charts during dyeing and finishing processes. The pH level can affect the color intensity and fastness of the dye. By carefully monitoring and adjusting the pH level, textile professionals can create vibrant and long-lasting colors to achieve the desired results.
These are just some of the many use cases of the pH level chart in various industries. But is that limited to industries only?
Maintaining a Balanced pH: Tips and Precautions
Maintaining a balanced pH isn’t just important for industries. It’s also crucial for our personal health. Here are a few tips and precautions to help you maintain a balanced pH:
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help maintain your body’s pH balance.
- Eat a balanced diet: Consuming too many acidic or alkaline foods can throw off your body’s pH balance.
- Test your soil: If you’re into gardening, regularly test your soil’s pH level to make sure it’s suitable for the plants you’re growing.
Remember, maintaining the right pH balance is all about moderation and regular monitoring.
Conclusion: The Impact of Understanding pH Balance on Our Lives
Understanding the pH scale isn’t just for science nerds. It has practical applications in our everyday lives. From the food we eat to the products we use, pH levels play a crucial role.
By understanding the pH scale, not only can you make more informed decisions, but you can also gain a greater appreciation for the subtle science that influences our world. So, the next time you sip your coffee or water your plants, remember the pH scale and the delicate balance it represents.
So there you have it, a comprehensive guide to the world of acidity and alkalinity. Whether you’re a science enthusiast or just a curious soul, we hope this guide has been both informative and entertaining. Happy pH balancing!